Yes, many tools and frameworks abstract complex math. However, understanding fundamentals like gradients and optimization can enhance your learning.
Understanding Hands-On Machine Learning
Machine learning has become one of the most influential technologies of our time, with advancements in deep learning significantly impacting the entire field of machine learning. It powers AI technology and applications we interact with daily, from recommendation systems to voice assistants, and its potential continues to grow. For data scientists, software engineers, and others who are new to this field, understanding and practicing hands-on machine learning is the key to unlocking its full potential. This approach allows individuals to move beyond theoretical knowledge and focus on building intelligent systems using machine learning and deep learning techniques to solve real-world problems.
Definition of hands-on machine learning
Hands-on machine learning refers to the practical application of machine learning concepts and techniques. Rather than focusing solely on theoretical understanding, it emphasizes working with real datasets, implementing machine learning algorithms, and using production-ready Python frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn. Popularized by authors like Aurélien Géron, especially through resources like his practical book Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow (2nd Edition), this approach equips beginners and seasoned practitioners alike to create deep learning systems, experiment with architectures like deep neural networks (deep neural nets), and tackle projects in computer vision, natural language processing, and more.
Why hands-on learning matters
Hands-on learning is a great way to understand machine learning because it connects theory with practice. It helps learners actively engage instead of just absorbing information passively.
- Bridging theory and practice: Hands-on learning transforms abstract concepts into tangible skills. For example, experimenting with support vector machines or random forests allows learners to see how these machine learning algorithms perform with real-world data. This practical exposure highlights nuances, like how data quality or feature engineering affects model performance, which may not be evident from theory alone. By engaging directly with these algorithms, learners develop an intuitive understanding of machine learning concepts, making it easier to internalize how they function in real-world scenarios.
- Building confidence: By working on practical projects, learners gain confidence in their ability to build and deploy machine learning systems. Tackling real problems — such as creating a classifier for email spam detection or a regression model for predicting housing prices — demonstrates how complex tasks can be broken down into manageable steps. Code examples and tutorials simplify the initial stages, helping learners feel less intimidated by the vastness of machine learning.
- Preparing for real-world applications: Hands-on experience ensures that learners can handle the entire process of a machine learning project, from preprocessing data to deploying a model into production environments. This holistic approach teaches critical problem-solving skills, such as debugging issues in TensorFlow 2 code, optimizing deep learning architectures, or integrating APIs for deployment. Real-world preparation also includes understanding collaboration tools like GitHub and managing the iterative nature of machine learning workflows.
What are the core concepts of hands-on machine learning?
Hands-on machine learning involves mastering several fundamental concepts:
- Machine learning: Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data and make decisions or predictions without being explicitly programmed. It uses algorithms — a set of instructions or rules — to identify patterns and relationships within data, allowing systems to improve their performance over time.
- Neural networks: Neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm inspired by the structure of the human brain. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes (digital “neurons”) that process and transform data to learn patterns and make predictions. Neural networks are the foundation of many advanced techniques, such as deep learning.
- Deep learning: Deep learning builds on neural networks by introducing multiple layers (deep neural networks) to extract intricate patterns from data. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) excel in image processing tasks, such as identifying objects in photos, while recurrent neural networks (RNNs) handle sequential data like text or time series. Transformers, a newer deep learning architecture, have revolutionized natural language processing by enabling powerful language models.
- Supervised learning: Supervised machine learning uses labeled datasets — data with predefined outcomes — to train models for specific tasks. For example, classification involves sorting data into categories, such as identifying spam emails, while regression predicts continuous values, like house prices. A foundational technique in this area is simple linear regression, which is an approachable starting point for beginners. Linear regression is a common example of a regression algorithm. Support vector machines (SVMs), which classify data by finding the best boundary to separate groups, are also commonly used in this category.
- Unsupervised learning: Unlike supervised learning, unsupervised machine learning deals with unlabeled data and aims to uncover hidden patterns or groupings. Algorithms like k-means clustering group similar data points, while autoencoders, a type of neural network, are used for tasks like anomaly detection and feature extraction. Feature extraction simplifies data by identifying the most relevant information for a task, making analysis more efficient. These methods are also valuable for exploratory data analysis (EDA), where visualizations and summaries help understand data trends and patterns, and dimensionality reduction, which makes massive datasets more manageable by reducing the number of variables while retaining essential information.
- Reinforcement learning: This approach trains models to make a sequence of decisions by rewarding positive outcomes and penalizing negative ones. Common in gaming and robotics, reinforcement learning involves an agent interacting with an environment to learn optimal strategies. Adaptive decision-making is made possible by techniques like Q-learning, which uses a table to store and update the value of actions based on rewards, and deep Q-networks, which use neural networks to approximate these values for complex environments.
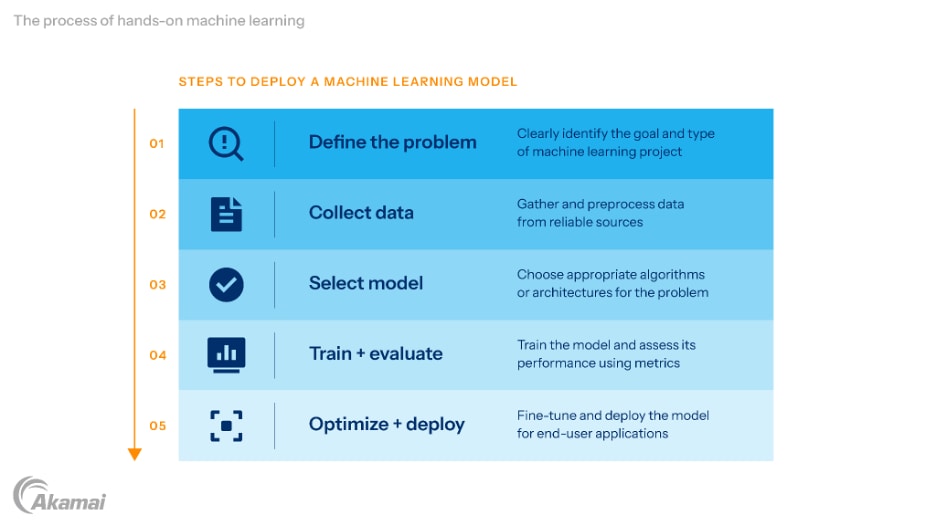
What is the process of hands-on machine learning?
Software engineers and data scientists engaged in hands-on machine learning will typically follow a structured process.
- Define the problem: Clearly identify the goal of the machine learning project, such as predicting stock prices or classifying images. Define measurable objectives and identify the type of problem — whether it’s classification, regression, or clustering.
- Collect and preprocess data: Gather datasets from reliable sources or platforms like GitHub. Use commands to download datasets and set up the project environment efficiently. Use tools like NumPy to preprocess and clean the data by addressing missing values, removing duplicates, and scaling features. For instance, ensuring data consistency can significantly improve the accuracy of classifiers.
- Select appropriate models: Choose machine learning algorithms or architectures based on the problem type. For image recognition, deep learning models like CNNs or transformers are ideal, while traditional classifiers like support vector machines work well for smaller datasets. Understanding the strengths of various algorithms is critical.
- Train and evaluate models: Train the model using frameworks like TensorFlow 2 or PyTorch. Evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and using a validation dataset help assess model performance. Techniques like cross-validation ensure robust evaluation by testing the model on multiple data splits.
- Optimize and deploy: Fine-tune the model for better performance by adjusting hyperparameters or incorporating regularization techniques. Deploy the final model using APIs or production-ready Python frameworks, ensuring the model can scale efficiently for large datasets or production use, and providing reliability for end user applications.
Tools and frameworks for hands-on machine learning
The right tools and frameworks are essential for successfully implementing hands-on machine learning projects, as they simplify complex processes and provide resources for experimentation and deployment.
- Python: Python is the most widely used programming language in data science and machine learning due to its user-friendly syntax, versatility, and extensive library support. Programming experience is especially helpful for leveraging these efficient tools productively. Libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib make data manipulation, analysis, and visualization seamless, while frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch build on Python’s strengths for machine learning.
- TensorFlow and TensorFlow 2: TensorFlow is a powerful open source framework developed by Google for building and training machine learning and deep learning models. TensorFlow 2, the latest version, simplifies the development process with an intuitive interface, “eager execution” for debugging, and native support for the Keras API, making it accessible for both beginners and experts.
- Keras: Keras is a high-level API built on TensorFlow that focuses on enabling quick prototyping of deep learning models. With its user-friendly interface and modular design, Keras makes it easy to create, train, and fine-tune neural networks, allowing developers to focus on innovation rather than technical complexity.
- Scikit-learn: Scikit-learn is a robust library designed for implementing traditional machine learning algorithms, such as support vector machines, decision trees, and random forests. It includes tools for data preprocessing, model evaluation, and feature selection, making it ideal for beginners and professionals working on structured data projects and developing practical machine learning programs.
- PyTorch: PyTorch, developed by Facebook, is a flexible and dynamic framework for deep learning. Its dynamic computation graph allows developers to modify models on the fly, which is particularly useful for research and experimentation. PyTorch also integrates well with popular machine learning workflows, enabling seamless deployment.
- Jupyter Notebooks: Jupyter Notebooks provide an interactive environment for writing, testing, and sharing code. They support the integration of code, visualizations, and narrative text into a single document, making them invaluable for exploring data, documenting processes, and collaborating on machine learning projects.
Hands-on projects
Hands-on projects and exercises provide practical exposure to machine learning and allow learners to apply their knowledge to solve real-world problems. Each project explores a unique domain and highlights critical machine learning techniques.
- Image classification with TensorFlow: Use the MNIST dataset to train a CNN for handwritten digit recognition. This project introduces concepts like deep neural networks and gradient optimization. It also allows learners to experiment with hyperparameter tuning to improve accuracy.
- Text sentiment analysis: Build a natural language processing model using RNNs or transformers. Use datasets of movie reviews to classify sentiments. This project helps learners understand tokenization, embeddings, and sequential modeling while exploring the versatility of language transformers.
- Recommendation systems: Create a model that suggests products or content based on user behavior. Frameworks like PyTorch can be employed for this task. Learners gain experience working with collaborative filtering and matrix factorization — critical for personalizing user experiences.
- Autoencoders for anomaly detection: Implement unsupervised learning to identify outliers in datasets. This project showcases the versatility of autoencoders, teaching participants how to encode and decode data efficiently while identifying patterns that deviate from the norm.
Challenges and how to overcome them
Challenges are an inherent part of machine learning, but addressing them effectively can lead to better outcomes and stronger skills.
- Data quality issues: Poor data quality can hinder model performance. Address this by thorough preprocessing and cleaning of datasets. For example, removing duplicate entries, filling in missing values, and normalizing data can significantly improve results. Leveraging tools like Pandas and NumPy ensures efficient preprocessing.
- Overfitting: Overfitting occurs when a model learns patterns and details specific to the training data, resulting in excellent performance on that data but poor generalization to new, unseen data. To address overfitting, techniques like regularization and cross-validation are used. Regularization discourages overly complex models, helping the model to generalize better to new data. Cross-validation divides the dataset into multiple subsets, training the model on some subsets while validating it on others. This iterative process ensures the model is evaluated on unseen data during training, providing a better measure of its performance and reducing the risk of overfitting.
- Rapidly evolving field: Machine learning evolves quickly. Staying updated with the latest tools and leveraging online resources is essential. Participating in forums and following advancements in frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch ensures ongoing learning. Seeking feedback from the community, such as suggestions, bug reports, and review comments, is crucial for staying current and continuously improving your work.
What are best practices for hands-on machine learning?
Adopting best practices ensures that machine learning projects are effective and efficient, leading to better outcomes and more robust systems.
- Start with fundamentals: Begin with basic concepts and gradually progress to advanced topics like artificial neural networks and reinforcement learning. A solid understanding of fundamentals sets the stage for tackling complex challenges.
- Experiment extensively: Test different architectures and frameworks to find the best fit for your project. Trying variations in algorithms or tweaking hyperparameters can uncover optimal solutions.
- Leverage community resources: Platforms like GitHub and O’Reilly Media provide invaluable resources, from code examples to in-depth tutorials. Engaging with the community also facilitates knowledge sharing and problem-solving.
- Focus on deployment: Ensure that models are production-ready by testing APIs and ensuring scalability. Deploying a model involves integrating it into real-world applications, requiring attention to performance, reliability, and user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Datasets like MNIST for image classification and IMDB for sentiment analysis are excellent starting points for hands-on machine learning.
Both frameworks are excellent. TensorFlow is great for production-ready systems, while PyTorch is preferred for research and flexibility.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.