The time required to train an AI model depends on factors like the size of the dataset, model complexity, hardware resources, and the optimization algorithm. It can range from minutes for small models on simple tasks to weeks for complex models like GPT or large-scale image recognition systems.
A comprehensive guide to AI training
Artificial intelligence (AI) has made incredible advances in recent years, transforming industries and reshaping how we live and work. AI systems now power tools and services that impact our daily lives, from personalized recommendations to voice assistants and beyond. At the heart of AI’s success is AI training — the process that allows AI systems to learn, adapt, and improve their capabilities over time. AI training underpins the development of cutting-edge technologies like generative AI, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning, enabling these systems to solve complex problems and create innovative solutions.
What is AI training?
AI training is the process of teaching artificial intelligence systems, including machine learning and deep learning models, to perform specific tasks. It involves using large datasets and sophisticated algorithms to help AI models learn patterns, solve problems, and make decisions. This process enables AI to make great strides in areas like robotics, decision-making, automation, generative AI, chatbots, computer vision, NLP, and other AI applications.
To achieve this, AI training uses iterative processes to fine-tune AI models. These processes include feeding the system with structured or unstructured data, applying optimization techniques, and adjusting parameters based on performance metrics. During training, the system refines itself by using feedback and validation results to enhance accuracy and avoid issues like overfitting. In reinforcement learning, the AI learns by improving its decision-making over time through trial and error, guided by positive or negative feedback, similar to human reinforcement behaviors. By leveraging advanced techniques in data science and software development, AI training enables models to continuously improve, making them adaptable to changing requirements and environments.
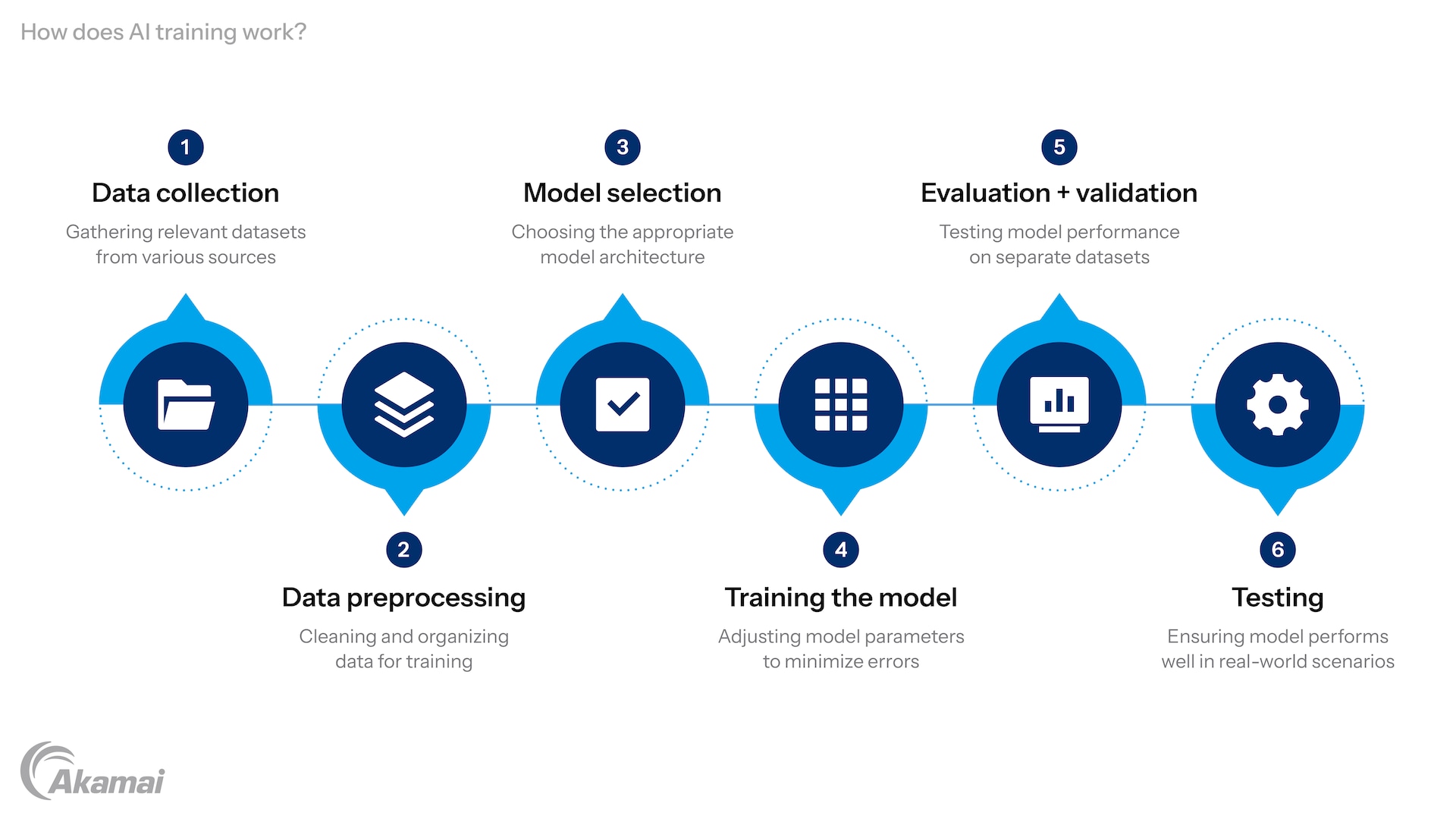
The process of AI training involves several key steps:
- Data collection: The first step is gathering datasets that are relevant to the task the AI will perform. These datasets may come from databases, documents, audio and video recordings, business interactions, social media, and other sources. Data scientists ensure that the data is comprehensive and diverse, making training more effective. By having a wide variety of data, AI systems can generalize better and handle a range of scenarios, which improves their performance and reliability in real-world applications.
- Data preprocessing: Collected data is often raw and unstructured. Data preprocessing cleans and organizes the information to make it suitable for training. Techniques like normalization and augmentation are applied to improve the quality of datasets. This step may also involve removing duplicates, filling in missing values, and converting data into formats that AI models can easily process. Effective preprocessing ensures that the training process is smooth and minimizes potential errors that could arise from low-quality input.
- Model selection: Choosing the right model depends on the task. For example, neural networks are effective for tasks involving deep learning, while simpler models might suffice for regression or optimization problems. Factors like the complexity of the task, available computational resources, and desired outcomes influence this decision. By selecting the appropriate model architecture, developers can optimize performance and efficiency, ensuring the AI system meets specific goals effectively.
- Training the model: During training, the model learns from the data by adjusting its parameters to minimize errors. This step requires powerful frameworks like TensorFlow and programming languages like Python to create and refine AI systems. Training involves running multiple iterations, or epochs, where the model fine-tunes its predictions based on feedback from the data. Optimization algorithms such as gradient descent play a crucial role in this process, allowing the model to progressively improve its accuracy.
- Evaluation and validation: AI models are tested on separate datasets to evaluate their performance. Metrics like accuracy and optimization scores help identify areas for improvement. Validation provides a checkpoint during the training process, ensuring that the model isn’t overfitting to the training data. By comparing predictions to actual outcomes, developers can tweak parameters or adjust datasets to enhance overall effectiveness.
- Testing: The final phase involves testing the AI system on new data to ensure it performs well in real-world scenarios. This step highlights how well the model generalizes to unseen data, ensuring its reliability and robustness. Testing often involves scenarios that simulate practical use cases, allowing developers to refine the system further before deployment. A well-tested AI model can operate efficiently in diverse environments, delivering consistent and accurate results.
The technology that underpins AI models and AI training
Several fundamental technologies and concepts form the foundation of AI and AI training.
- Machine learning: Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on building systems capable of learning from data and improving over time without being explicitly programmed. It powers a wide range of applications, from recommendation engines to predictive analytics.
- Neural networks: Neural networks mimic the structure of the human brain, consisting of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers. These networks are the backbone of many AI systems, enabling them to identify patterns and make data-driven decisions.
- Deep learning: Deep learning, a branch of machine learning, uses neural networks with multiple layers to process and analyze complex data. This technology excels in areas like image and facial recognition, natural language processing, and speech generation.
- Decision trees: Decision trees are a fundamental machine learning algorithm that function like flowcharts, where each node represents a decision point based on input features. They are widely used in training processes for tasks such as loan approvals and other practical scenarios.
- AI models: AI models are mathematical representations of data used to make predictions or decisions. They range from simple linear regression models to advanced large language models.
- Large language models (LLMs): LLMs, such as ChatGPT, are a type of AI model trained on massive datasets to understand and generate text. They are widely used in applications like chatbots, content generation, and customer support.
- Natural language processing (NLP): NLP focuses on enabling AI systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Applications include chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis.
- Parameters: Parameters are adjustable values within an AI model that influence its predictions. During training, parameters are adjusted and optimized to minimize errors and improve the model’s accuracy.
What are types of AI training?
There are various approaches to AI training, each tailored to specific needs:
- Supervised learning: In supervised learning, the model is trained on labeled data, where the correct answers are provided during training. This method is widely used for tasks like image recognition, speech recognition, and NLP. It allows the model to learn from examples, enabling it to make accurate predictions for similar data it hasn’t seen before.
- Unsupervised learning: Here, the AI discovers patterns and relationships in unlabeled data, with no explicit instructions on what to look for. Applications include clustering, where data is grouped into similar categories, and anomaly detection, which identifies unusual or rare occurrences. This approach is valuable for uncovering hidden insights and making sense of large, unstructured datasets.
- Semi-supervised learning: Semi-supervised learning combines both labeled and unlabeled data to train models more efficiently. It serves as a middle ground between supervised and unsupervised learning, leveraging a small amount of labeled data along with a larger pool of unlabeled data. This technique is especially useful when labeling data is expensive or time-consuming, allowing AI systems to achieve better performance with less manual effort.
- Reinforcement learning: Reinforcement learning involves training AI systems to make decisions by rewarding desired outcomes and penalizing undesirable ones. This approach is common in robotics, gaming, and optimization problems in which the system must learn by trial and error. By interacting with its environment and receiving feedback, the AI can refine its decision-making process over time, achieving better performance and efficiency.
What are tools for AI training?
AI training relies on specialized tools and technologies.
- Frameworks: Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch provide the infrastructure needed to build and train AI models. These frameworks simplify complex tasks like creating neural networks, implementing optimization algorithms, and managing workflows. Training complex AI models with these frameworks often requires significant infrastructure requirements, such as high compute power and ample storage, to efficiently process large datasets and support advanced model architectures. By using these frameworks, developers can save time and focus on refining their AI solutions for better performance.
- Programming languages: Python is the most popular language for AI training, thanks to its simplicity and robust libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Scikit-learn. It allows developers to write clean and efficient code, enabling quick prototyping and testing of AI models. Strong coding skills are essential for selecting and using AI training tools efficiently. Other languages like R and Julia are also used in specific applications, but Python remains the go-to choice for most AI projects.
- Cloud services: Platforms like Akamai, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer scalable resources for handling large workloads and datasets. These cloud services provide powerful computational capabilities, including GPU and TPU acceleration, to speed up training processes. They also address infrastructure requirements that enable collaboration and storage, making them ideal for both small teams and large organizations.
- Educational tools: Interactive learning paths, webinars, and AI courses make AI training accessible to learners of all levels. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer hands-on training and certification in AI concepts and AI tools, while webinars hosted by industry leaders and AI experts provide valuable insights into the latest developments. These tools help individuals learn AI by building foundational AI skills and stay updated on cutting-edge computer science technologies in AI and machine learning.
What are best practices for AI training?
To achieve optimal results, follow these best practices:
- Use diverse datasets: A diverse dataset ensures that the AI system can perform well across different scenarios, reducing biases and improving reliability. By including data from various demographics, environments, or conditions, developers can make their AI models more versatile and fair. Diversity in datasets also helps the AI system better handle real-world complexities.
- Monitor training metrics: Tracking metrics like loss, accuracy, and precision helps identify issues early in the training process. By analyzing these metrics during training, developers can detect potential problems, such as overfitting or underfitting, and make adjustments accordingly. Continuous monitoring ensures that the model’s performance improves steadily and predictably.
- Adopt transfer learning: Pretrained models can save time and resources, especially when dealing with limited data. Using transfer learning allows developers to build on existing AI models trained on similar tasks, reducing the need for extensive new training. This approach is particularly beneficial in applications where gathering large datasets is challenging.
Benefits of AI training
The benefits of AI training are far-reaching, offering transformative potential for both businesses and individuals. By investing in the AI model training process, organizations can develop AI models that recognize patterns, make decisions, and deliver highly accurate outputs based on massive amounts of relevant data. This ability to process and analyze large amounts of information not only boosts output accuracy but also enhances customer experiences by providing faster, more personalized solutions.
What are the challenges with AI training?
While AI training offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges:
- Data quality: Poor-quality datasets can lead to inaccurate results and biased outcomes. Cleaning and curating data requires significant time and resources, and even small errors in the data can affect the AI’s performance. Ensuring data diversity and accuracy is crucial to building reliable and fair AI systems.
- Computational demands: Training complex models requires high-performance hardware and significant energy resources. Access to GPUs, TPUs, or powerful cloud infrastructure is often essential, but these resources can be expensive and environmentally demanding. Efficiently managing workloads and exploring energy-efficient algorithms can help address these challenges.
- Ethical concerns: Addressing biases in AI models and ensuring privacy remain ongoing challenges. Biased training data can result in unfair or discriminatory outcomes, while privacy issues may arise when using sensitive information. Developers must actively identify and mitigate biases, and adhere to data protection laws to build ethical AI systems.
What is the future for AI training?
The future of AI training is promising, with trends like self-paced learning, prompt engineering, and cutting-edge techniques revolutionizing the field. Self-paced learning allows individuals to acquire AI skills at their own convenience, increasing accessibility and inclusivity. Prompt engineering is advancing how large language models, like ChatGPT, interact with users by refining input instructions for more accurate and context-aware outputs.
Innovations in large language models and advancements in areas like computer vision and natural language processing will continue to shape AI systems and applications. Additionally, federated learning and distributed AI training are emerging as solutions for privacy-preserving AI development. These approaches allow models to learn from decentralized data sources while keeping sensitive information secure. The integration of energy-efficient methods and ethical frameworks in AI training will further ensure the responsible growth of AI technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Data augmentation involves artificially increasing the size and diversity of the training dataset by applying transformations like flipping, rotating, or cropping images or altering text data with synonyms or paraphrasing. This helps improve model generalization and reduces the risk of overfitting.
Transfer learning is a technique where a pretrained model on one task is fine-tuned for a different but related task. It’s especially useful when the target dataset is small, as the model leverages the knowledge from its initial training to achieve better performance on the new task.
Overfitting occurs when a machine learning model learns the training data too well, capturing noise or irrelevant patterns instead of generalizing from the data. This results in excellent performance on the training dataset but poor performance on new, unseen data. Overfitting can be mitigated through techniques like cross-validation, regularization, and using simpler models.
Gradient descent is an optimization algorithm used in training machine learning models. It helps minimize the error or loss function by iteratively adjusting model parameters (weights and biases) in the direction that reduces the loss. The adjustments are proportional to the gradient of the loss function with respect to the parameters, ensuring the model improves with each step.
Yes, natural language processing (NLP) and LLM models often support multiple languages. Multilingual models, such as GPT, are trained on diverse datasets covering multiple languages. However, their proficiency may vary depending on the quantity and quality of data available for each language in the training process.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.