An AI model is a mathematical framework designed to simulate cognitive processes like learning, reasoning, and decision-making. These models are trained on data to perform specific tasks, such as recognizing images or generating text.
Understanding Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large language models (LLMs) are one of the most exciting advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). These powerful machine learning AI models are designed to understand and generate human language, mimicking how people communicate. They are reshaping how we use technology, enabling applications that were once thought impossible. From improving chatbots to automating text generation, large language models are revolutionizing the way businesses, researchers, and individuals interact with AI systems.
By processing vast amounts of data, these models can analyze context, understand grammar, and even create text that feels human. This ability makes them valuable across countless applications, from content creation to problem-solving. Whether you’re using a chatbot for customer service or employing automation tools for workflows, LLMs ensure the experience is seamless and natural. As their capabilities grow, large language models continue to unlock new possibilities in fields as diverse as healthcare, education, and computer programming.
Large language models: A definition
An LLM, or large language model, is a type of AI model trained to process and generate human-like language. These models use advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze and generate text based on patterns found in large datasets. By learning from trillions of words, LLMs understand context, grammar, and meaning, making them highly effective for tasks like summarization, translation, and content creation. A key method used to train these models is self-supervised learning, which enables them to learn language patterns and semantics from vast amounts of unlabeled data.
Large language models are built on the principles of deep learning and are fine-tuned for specific tasks, making them highly adaptable to various domains. As foundation models, LLMs serve as versatile bases that can be fine-tuned for various language tasks. They excel at working with unstructured data, which makes them especially useful for natural language processing (NLP). For example, models like GPT-3 and GPT-4 set the standard for generating coherent text by predicting the next word in a sentence. Additionally, LLMs use embeddings, which are numeric representations of words and phrases, enabling them to capture semantic relationships. This combination of scale, precision, and versatility defines their unique role in modern AI applications.
How large language models work
Understanding how LLMs work requires an understanding of their underlying technologies, advanced deep learning architectures such as transformers, and training processes. These elements enable large language models to process sequential data, such as sentences and paragraphs, allowing them to understand context and meaning, and to generate human-like language efficiently and accurately.
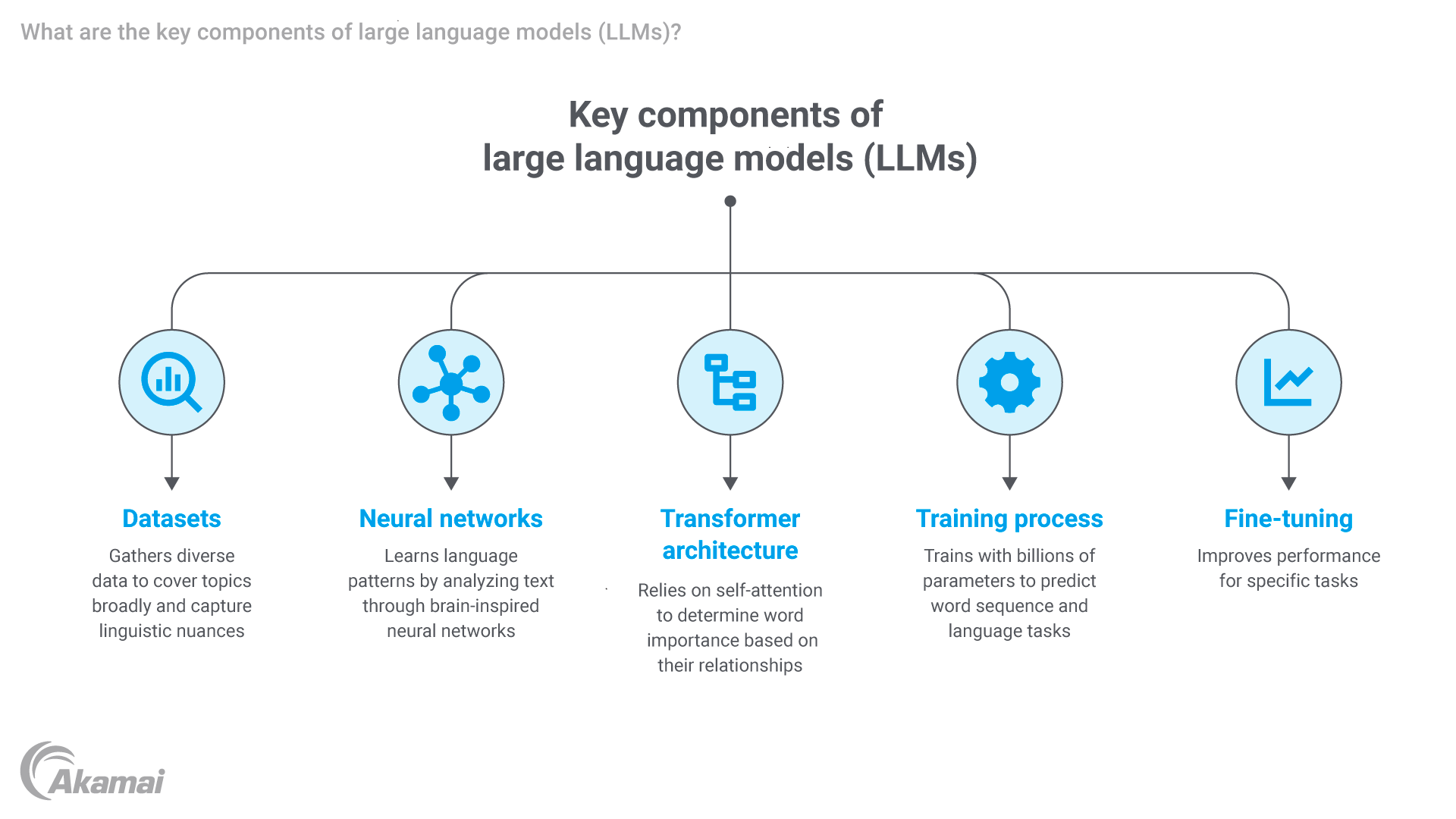
Large language models rely on several key technologies.
Datasets: Datasets are vast libraries of information like books, articles, websites, and other forms of text that large language models learn from. By analyzing this training data, the LLM starts recognizing patterns, such as how words are used together or how sentences flow.
Neural networks: At the heart of an LLM is a system called a neural network. This is a web of connected, decision-making “nodes” that work together to analyze data. Each node looks at part of the information and passes its findings to others, gradually building a bigger picture. This system mimics how human brains process information, which is why it’s called a neural network. Neural networks allow the model to identify relationships in the data and “understand” language at a deeper level.
Transformer architecture: One key innovation in LLMs is something called the transformer model, which helps the system focus on the most important parts of text. For example, if you’re reading a book, you might pay extra attention to the main characters or plot twists while skimming over less relevant details. Transformers work in a similar way. They use a method called self-attention, which allows the model to prioritize and understand the context of words in a sentence.
Transformers also use two main parts:
- Encoders, which process input text to understand its meaning. For instance, encoders handle tasks like sentiment analysis to figure out if a sentence is positive or negative.
- Decoders, which generate new text, such as writing a story or answering a question, by predicting the next token in a sequence to create coherent and contextually appropriate text.
Different models use these parts differently. For example:
- BERT (a type of LLM) mainly uses encoders to analyze and understand text.
- GPT models rely on decoders to create new text.
Embeddings: To make sense of words and their meanings, LLMs use embeddings — a technology for translating words into numbers that capture their meaning and relationships. For example, the words “dog” and “puppy” will have numbers that are closer to each other because they are similar in meaning, while “dog” and “car” will be further apart. Embeddings allow the model to understand not just what words mean but also how they fit into different contexts.
What is the training process for LLMs?
The training of LLMs is an intensive and iterative process that involves several steps:
- Training phase: LLMs process vast datasets containing trillions of words to learn the structure and meaning of human language. Advanced algorithms, including self-attention mechanisms, help the model identify relationships between words and phrases. Self-learning and self-supervised learning enable LLMs to learn language patterns and semantics from unlabeled data by predicting parts of text and understanding context through large unannotated datasets.
- Fine-tuning: After pretraining, LLMs can be fine-tuned on domain-specific tasks, such as translation, summarization, or code generation. This step tailors the model’s capabilities to meet specific needs. Few-shot learning allows LLMs to adapt to new tasks with only one or a few examples, making them flexible for specific use cases with minimal instruction.
- Optimization: During training, the model continually refines its predictions using feedback to improve accuracy and relevance. Dependencies within sentences are identified to enhance linguistic comprehension. Reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) is used to further refine model outputs, reduce biases, and improve safety by aligning responses with human preferences.
How do LLMs function?
LLMs generate and analyze text using the knowledge acquired during training.
- Text generation: By predicting the next word in a sequence, LLMs create coherent and contextually appropriate text. They can generate contextually relevant responses tailored to the user’s input, which powers applications like chatbots, content creation, and tutorials.
- Zero-shot learning: Advanced LLMs, like GPT-4 and GPT-5, can perform tasks they have not explicitly been trained on by leveraging their broad general knowledge base.
- Attention mechanisms: These mechanisms allow LLMs to focus on the most relevant parts of the input, ensuring that outputs are accurate and contextually meaningful. This enables LLMs to answer questions effectively by identifying and using the most pertinent information from the input.
What can LLMs do?
Large language models possess a wide array of skills that enable them to perform diverse tasks effectively.
- Text generation: LLMs can create articles, emails, and other written content. By automating repetitive tasks, they can make workflows faster and more efficient.
- Conversational AI: Systems like ChatGPT and Claude utilize large language models to enable human-like interactions. These models make virtual assistance and customer service more natural and engaging.
- Programming support: Tools like OpenAI’s Codex and Meta’s open source LLM, Llama, assist developers in generating code, debugging, and learning programming languages. GitHub Copilot, for example, leverages LLMs to streamline software development processes. LLMs can also generate code based on natural language instructions, supporting automatic programming and code completion.
- Language translation: Models such as Google’s PaLM facilitate accurate translations between languages, enhancing global communication.
- Content creation: From tutorials to creative writing, large language models are versatile tools for producing high-quality, domain-specific content tailored to different audiences.
- Domain-specific tasks: Fine-tuning allows LLMs to specialize in specific industries, such as finance, law, and education, broadening their usefulness.
- Zero-shot capabilities: Advanced LLMs can perform tasks they haven’t been explicitly trained for, showcasing flexibility and adaptability.
How are large language models used across industries?
Large language models are reshaping industries by applying their advanced capabilities to solve real-world challenges and streamline processes. Here’s how they’re making an impact:
Healthcare. LLMs assist in summarizing patient data by processing large volumes of medical records, making it easier for doctors to review a patient’s history quickly. For instance, an LLM can highlight critical information such as allergies or past diagnoses from lengthy reports. They also help in supporting diagnoses by analyzing medical literature or symptoms to provide potential insights, acting as a supplemental tool for physicians. Additionally, they automate administrative tasks like generating discharge summaries or transcribing doctor-patient conversations, freeing up time for healthcare providers to focus on patient care.
Technology and software development. In software development, tools like GitHub Copilot, powered by LLMs, help developers write code by predicting what comes next as they type, much like autocomplete on your phone. This allows coders to work faster and focus on solving higher-level problems. LLMs also aid in debugging code, suggesting fixes or identifying potential errors in real time. For instance, if a developer encounters a syntax issue, the LLM can recommend corrections or even explain why a particular code segment isn’t functioning as intended.
Education. LLMs are transforming education by creating interactive learning tools, such as chatbots that answer student questions or simulate real-world problem-solving scenarios. For example, a history student could “interview” an LLM acting as a historical figure. They also automate grading, allowing teachers to focus on instruction rather than paperwork. Furthermore, large language models help develop personalized study materials, tailoring quizzes or summaries based on a student’s learning pace and style.
Customer service. Conversational AI systems powered by large language models are revolutionizing customer support by delivering quick, accurate responses to customer queries. For instance, a chatbot for an ecommerce site can help users track orders, suggest products, or resolve common issues like refund requests. LLMs also provide context-aware interactions, meaning they can remember past questions in the conversation and offer more natural, human-like communication.
Content and media. LLMs streamline the content creation process in industries like journalism, marketing, and entertainment by automatically generating articles, ad copy, or even scripts. For instance, an LLM can draft a first version of a news article based on provided data, allowing journalists to focus on editing and analysis. In marketing, LLMs are used to brainstorm creative taglines or campaign ideas, saving time and boosting productivity for content teams.
Finance. In finance, LLMs analyze large datasets to identify patterns and trends, helping companies make informed decisions. An LLM can sift through market data to highlight investment opportunities or detect unusual spending that could indicate fraud. They also assist in generating detailed reports, translating complex data into easy-to-understand summaries for stakeholders.
Global communication. By enabling seamless translations, LLMs make it easier for businesses and individuals to communicate across language barriers. An LLM can help to instantly translate emails or documents between English and Mandarin while preserving context and tone. Additionally, these tools enhance multilingual collaboration by allowing teams from different regions to share ideas without misunderstandings, fostering global partnerships.
APIs and AI integration. LLM-based APIs, such as those offered by Microsoft or OpenAI, allow businesses to embed advanced AI capabilities into their applications without building models from scratch. For example, a retail company can use an LLM API to power a virtual shopping assistant in their app. These APIs also enable developers to customize AI for specific use cases, like creating tools for legal document analysis or personalized product recommendations.
What are the challenges and limitations of LLMs?
Despite their benefits, LLMs face several challenges:
- Biases: Since LLMs learn from training data, they may inherit biases present in the datasets. This can lead to unintended discrimination or reinforce stereotypes, raising ethical concerns that need to be addressed.
- Computational cost: Training and running LLMs require significant computational resources, which makes them both expensive and energy-intensive. This has implications for environmental sustainability and accessibility for smaller organizations.
- Factual inaccuracies: LLMs sometimes generate incorrect or nonsensical information, a phenomenon known as hallucination. This can undermine trust in their outputs, especially in critical applications like healthcare or finance.
- Ethical risks: The misuse of LLMs for spreading misinformation, generating harmful content, or automating unethical practices poses serious ethical challenges. These risks emphasize the need for responsible AI development and usage.
What is the future of LLMs?
The future of LLMs currently involves several trends.
- Smaller, more efficient models: Researchers are exploring ways to create smaller models that require fewer resources while maintaining high performance. This could make LLMs more accessible and sustainable.
- Multimodal capabilities: Future LLMs will likely integrate text with other data types, such as images, audio, and video. This evolution will expand their applications to fields like multimedia analysis and virtual reality.
- Improved accuracy: Ongoing research aims to reduce biases and hallucinations in LLM outputs, enhancing their reliability and trustworthiness for users.
- Ethical frameworks: Developing comprehensive ethical guidelines and oversight mechanisms will ensure responsible AI applications, mitigating risks associated with misuse and unintended consequences.
- Foundation models: LLMs will continue to evolve as foundation models, supporting a wide range of AI applications and use cases. Their adaptability and scalability will make them integral to future technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions
LLMs are a subset of AI models that specialize in natural language processing (NLP). They enable machines to understand, generate, and interact with human language, which is the core focus of NLP.
Generative AI refers to AI systems that create content, such as text, images, or audio, based on learned patterns. LLMs are a type of generative AI specifically focused on text generation and natural language understanding.
A generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) is an LLM that generates text using transformer architecture. It is pre-trained on extensive datasets and fine-tuned for specific tasks, excelling in text generation and natural language applications.
LLMs process data by tokenizing it into smaller components, such as words or sub-words, and analyzing the relationships between these tokens using self-attention mechanisms. This enables them to understand context and meaning within the text.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.