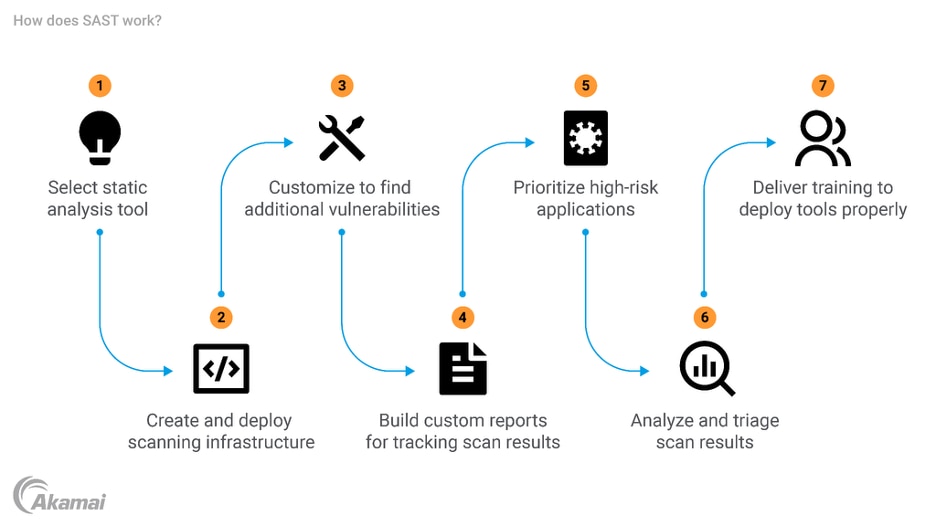
Before we get into when SAST should be performed, let’s first answer the question: What is SAST?
SAST, or static application security testing, is an important process that takes place in the early stages of the software development process, usually around the same time the code for the software program is written. It’s easily woven into the development process and the CI/CD pipeline.
An API security checklist should be used during SAST to ensure every step of the process is completed and verified. Following API security best practices also ensures all issues are efficiently tracked and reported. When issues are found, teams should work together to quickly address them so processes are performed on time and as securely as possible.