Out-of-band API security protects communication channels and interactions outside the typical request–response process. Unlike inline security, which operates within the API’s direct communication path, out-of-band methods monitor and secure alternate pathways, offering broader visibility and protection against covert threats.
Out-of-band API security focuses on safeguarding communication channels outside the standard request–response mechanism, making it effective against attacks that exploit covert or hidden channels.
The concept of out-of-band API security centers on protecting the transmission and exchange of information within APIs through methods beyond the typical request–response method. This involves incorporating extra layers of defense to defend against any potential attacks or weaknesses that may not be addressed by conventional in-band security methods.
In conventional API communication, the client initiates a request to the server, which then handles the request and delivers a response through the same means. In these cases, security precautions typically center around verifying requests, granting access permissions, encrypting data transmission, and safeguarding against common web vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS) or SQL injection.
Standard measures alone can’t effectively prevent some attacks. For example, out-of-band attacks utilize alternative communication methods or hidden channels that aren’t part of the normal request–response process, allowing them to bypass current security measures.
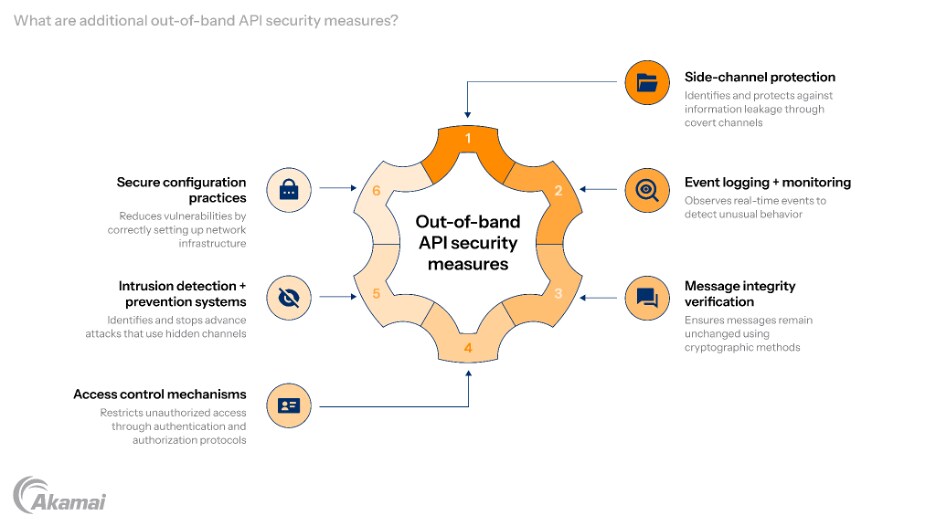
To address this gap, out-of-band API security employs additional protective measures:
Side-channel protection: It’s essential to identify and protect against potential side channels that could lead to the leakage of sensitive information during an API transaction. One way to do this is by monitoring timing inconsistencies between various aspects of an application’s behavior, which can reveal covert channels used by attackers to transmit data.
Event logging and monitoring: By incorporating thorough logging techniques, we have the ability to observe real-time events taking place within APIs, surpassing the usual HTTP traffic records. Examining these records enables us to identify unusual behavior or unauthorized efforts to access them that could signal out-of-band attack methods.
Message integrity verification: By making sure that messages remain unchanged, we can prevent any unauthorized modifications to important information shared between systems during API transactions. One way to achieve this is by using cryptographic methods, like digital signatures, which can confirm the legitimacy and integrity of messages sent through alternate channels.
Access control mechanisms: By enforcing access control policies, unauthorized individuals are unable to misuse alternate communication channels for malicious activities. By incorporating effective authentication methods and detailed authorization protocols, access rights are restricted according to the user’s specific circumstances or role, thus protecting against external attacks.
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS): By implementing IDPS systems designed specifically for out-of-band security, advanced attacks that use hidden channels or communication paths that aren’t adequately protected by traditional security measures can be identified and stopped.
Secure configuration practices: Implementing secure configuration practices for APIs reduces the risk of potential vulnerabilities that could be taken advantage of through out-of-band attacks. This involves correctly setting up the network infrastructure, application servers, firewalls, and any other elements involved in API communication.
Benefits of out-of-band API security
Utilizing out-of-band API security offers various advantages that strengthen the overall safeguarding and durability of APIs against sophisticated risks. Here are some advantages of implementing out-of-band security measures:
- Protection against hidden attacks: The main goal of out-of-band API security is to protect communication channels that aren’t part of the regular request–response process. This type of security is particularly effective against attacks that take advantage of hidden or secret channels. By actively monitoring alternate paths or side channels, companies can identify and stop attacks that may bypass standard in-band security methods.
- Defense against advanced threats: The inclusion of out-of-band security provides an additional level of protection against advanced methods of attack, such as stealing data, injecting commands, or infiltrating a system. This helps to reduce the dangers posed by attacks that use nontraditional methods to evade detection.
- Improved incident response: Organizations can improve their ability to identify unusual or malicious behavior that falls outside of typical network traffic patterns by implementing out-of-band protections. With enhanced logging and monitoring features, they can quickly detect and respond to potential incidents by obtaining useful information about suspicious activity from these extra sources.
- Data leakage prevention: Out-of-band API security measures are implemented to detect any possible channels through which sensitive data may be unintentionally exposed during interactions between systems within an API ecosystem. By identifying and securing these side channels, the risk of unauthorized access to important data is minimized.
- Secure communications validation: By incorporating out-of-band security measures, systems involved in API communications can conduct thorough validation and integrity checks on exchanged messages. This helps to guarantee the authenticity of messages from start to finish and reduces the possibility of tampering throughout the transaction process.
- Additional access control measures: Incorporating access control mechanisms beyond standard boundaries improves authorization policies by expanding their coverage to include unconventional communication paths utilized by APIs. This allows for more detailed controls based on user context or roles specific to each channel, minimizing the possibility of unauthorized access attempts through alternate means.
- Compliance requirements: Numerous regulatory frameworks and industry standards stress the significance of thorough security measures, such as out-of-band protections. By implementing these precautions, organizations can ensure compliance with data privacy, security, and industry regulations.
- Reducing false positives: Including out-of-band security provides an additional layer of protection in identifying threats by checking for consistent signals across various channels. This analysis across multiple channels aids in decreasing false alarms in threat detection systems, allowing for more precise identification of actual threats, and reducing unnecessary disturbances caused by false alerts.
Out-of-band API security vs. agent-based API security
Out-of-band API security and agent-based API security are two distinct approaches to protecting APIs, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. Here’s a comparison between the two:
The main focus of out-of-band API security is to protect communication channels and data flows that occur outside of the typical request–response process. This involves adding extra layers of defense to prevent attacks or weaknesses that normal in-band security methods may not detect.
On the contrary, agent-based API security utilizes specialized software agents that are installed on servers or endpoints within an API ecosystem. These agents are responsible for closely monitoring, safeguarding, and orchestrating the interactions of the APIs.
The decision to use either out-of-band API security or agent-based API security is determined by individual needs, the complexity of the infrastructure, and the level of cybersecurity risk. When choosing, organizations should take into account factors like the desired amount of visibility and control over protected endpoints or channels. Here’s a list of additional considerations to review:
- Deployment complexity: Agent-based solutions involve the installation of software agents on various systems within the API infrastructure, while out-of-band security focuses on securing external communication channels.
- Resource consumption: Continuous monitoring and processing of data by agents can deplete system resources. Proper management of agent deployment is crucial to prevent any negative effects on performance.
- Scalability: The scalability of agent-based solutions may be hindered when handling a high volume of endpoints, thus necessitating strategic planning and supervision.
Web application security: The role of out-of-band API security
Out-of-band API security plays a crucial role in securing web applications by safeguarding API communications outside of traditional request–response workflows. This approach addresses vulnerabilities often overlooked by standard inline methods, ensuring comprehensive protection for web apps. By identifying misconfigurations, monitoring API traffic, and implementing secure access controls, out-of-band security fortifies the connectivity between APIs and web applications. Enhanced logging and real-time analysis further strengthen application security, making this method essential in a cloud-driven world.
Key use cases for out-of-band API security
- Preventing data leakage: By detecting hidden side channels and ensuring message integrity, out-of-band security mitigates risks of unauthorized data exposure in APIs.
- Mitigating advanced threats: Out-of-band protections are effective against sophisticated attacks, such as API endpoint exploitation or covert command injections.
- Enhancing workflow integrity: Secure connectivity between APIs and systems ensures that workflows remain robust, reducing disruptions from misconfigurations or malicious actions like malware.
- Cloud security: With growing adoption of cloud-based services, out-of-band API security offers additional safeguards for cloud-hosted APIs, ensuring compliance and reducing vulnerability to attacks targeting API gateways.
API endpoints and traffic monitoring for better application security
Monitoring API endpoints and traffic is essential for robust application security and API protection. Out-of-band API security enhances visibility into API activity, detecting anomalies that may signal unauthorized access or misuse. This includes observing endpoint behavior, identifying unexpected spikes in API traffic, and validating access token exchanges. Furthermore, integrating these insights into workflows through automated alerts and actionable intelligence improves an organization’s ability to secure both on-premises and cloud-based APIs.
Frequently Asked Questions
By safeguarding against hidden channels and side-channel attacks, out-of-band security detects unauthorized data transmissions and ensures message integrity through cryptographic techniques, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Yes, out-of-band API security complements existing API gateways by providing additional layers of protection, monitoring, and threat detection. This ensures a more comprehensive approach to API security without disrupting current configurations.
While out-of-band API security doesn’t require inline changes or agents, proper setup of monitoring tools and secure configuration practices is essential to ensure effectiveness and seamless integration into workflows.
Cloud APIs are often exposed to a wide range of threats due to their accessibility. Out-of-band API security enhances cloud security by monitoring traffic, ensuring endpoint integrity, and addressing vulnerabilities specific to cloud-based architectures.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.